Frequency
Definition: The main frequency is the frequency of the electrical power supply in an AC-based power grid and is specified in the unit of measurement Hertz (Hz).
Why are there different grid frequencies around the world?
In Europe, Asia and Australia, a large part of Africa and parts of South America, a general grid frequency of 50 Hertz is used. In North America, on the other hand, 60 Hertz is common. This difference is due to historical reasons: When the first electricity grids emerged at the end of the 19th century, a dispute arose between proponents of AC voltage and advocates of DC voltage on the one hand. On the other hand, different technological bases in America and Europe led to different frequencies being established in the AC voltage range: 60 hertz in America and 50 hertz in Europe. These differences still exist today, although there are no necessary technical reasons for them. In Japan, different grid frequencies still exist today for historical reasons: 50 Hertz in the eastern part, which was supplied with generators from Germany in 1895, and 60 Hertz in the western part, for which generators were supplied from the USA.
Standardization or conversion to direct current is not seen as profitable in the short term, which is why global differences remain.
Due to the historical differences in grid frequencies, components of industrial systems must fit the local conditions.
Most equipment suppliers offer components for both grid frequencies.
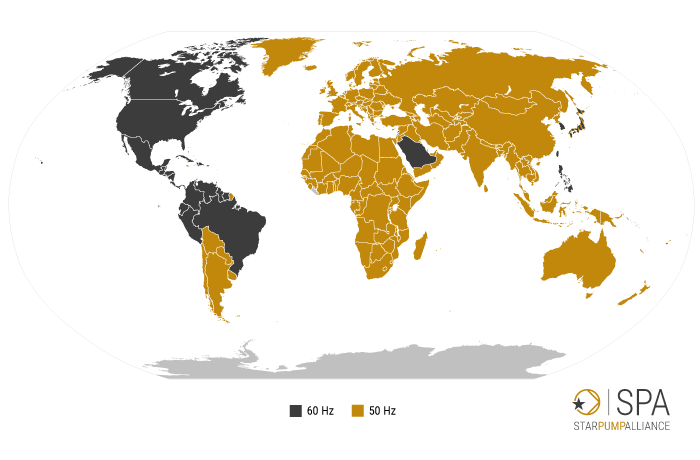
Different network frequencies are used around the world.