What is a Centrifugal Pump and How Does It Work
Centrifugal pumps are a fundamental component in various industries, providing a reliable method for moving fluids through pipelines. According to John Smith, a renowned expert in fluid mechanics, "Centrifugal pumps are the heartbeat of many industrial processes, enabling efficient fluid transport and system reliability." Understanding how a centrifugal pump operates is essential for engineers, technicians, and maintenance personnel who rely on these devices for effective system performance.
At its core, a centrifugal pump uses rotational energy to create fluid motion, utilizing an impeller to increase the velocity of the fluid and subsequently convert that velocity into pressure. This mechanical process is crucial in applications ranging from agricultural irrigation to chemical processing, where efficient fluid management is vital for operational success. By examining the principles, applications, and maintenance of centrifugal pumps, professionals can ensure optimal function and longevity in their respective systems.
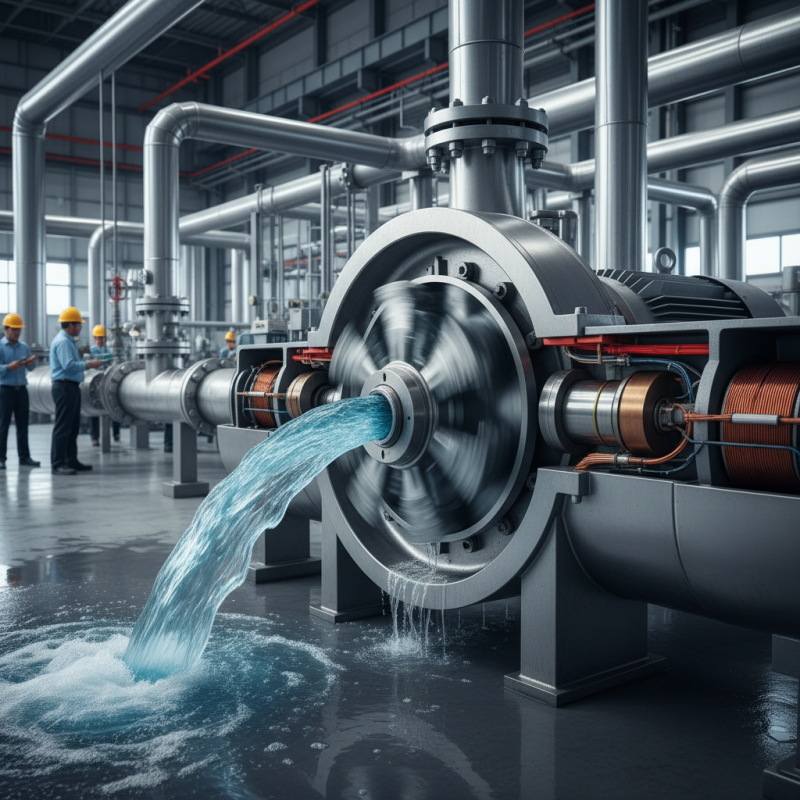

What is a Centrifugal Pump?
A centrifugal pump is a mechanical device specifically designed to move fluids by converting rotational energy to hydrodynamic energy. It achieves this through the use of a rotating impeller, which generates centrifugal force. As the impeller spins, it creates a pressure difference that causes the liquid to be drawn into the pump from the inlet, moves outward through the impeller, and eventually exits through the discharge. This mechanism makes centrifugal pumps highly effective for a wide range of applications, including water supply, irrigation, and industrial processes.
When selecting a centrifugal pump, it’s crucial to consider factors such as flow rate, head pressure, and the specific characteristics of the fluid being pumped. For instance, fluids that are viscous or contain solids may require specialized impellers or designs to ensure optimal performance and reduce wear on the pump components.
Tip: Always check the pump's operating curves provided by manufacturers to ensure it meets your specific requirements. Additionally, regular maintenance and monitoring of the pump can help prolong its lifespan and efficiency, preventing costly downtime or replacements.
Principles of Operation for Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps operate on the fundamental principle of converting rotational energy into kinetic energy to facilitate fluid movement. At the core of this process is the impeller, a rotating component that serves to draw fluid into the pump and increase its velocity. As the impeller rotates, centrifugal force expels the fluid outward, generating a pressure difference that causes the fluid to flow through the pump and into the discharge pipe. This dynamic interaction between the impeller and the fluid is what primarily drives the operation of a centrifugal pump.
The efficiency of a centrifugal pump is influenced by a range of factors, including the design of the impeller and volute, fluid viscosity, and inlet conditions. The volute casing, which houses the impeller, plays a crucial role in transforming the fluid's kinetic energy into pressure energy as it moves outward. Moreover, ensuring proper priming and maintaining appropriate flow rates are essential for optimal pump performance. Variations in impeller design can further tailor the pump's operation to accommodate different applications, allowing for a wide range of operational versatility in various industries.
Components of a Centrifugal Pump System
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in various industrial applications, and understanding their components is essential for effective operation and maintenance. The primary components of a centrifugal pump system include the impeller, volute, motor, seals, and bearings. The impeller is a rotating component that imparts kinetic energy to the fluid, increasing its velocity. According to the Hydraulic Institute, impellers can vary in design, including open, closed, or semi-closed configurations, each providing different flow characteristics suited for specific applications.
The volute is another critical part of the system. It serves to convert the kinetic energy of the fluid, produced by the impeller, into pressure energy. As fluid exits the impeller, it enters the volute, which gradually expands to reduce the fluid velocity, thus increasing pressure. Engineering reports indicate that an optimally designed volute can enhance the overall efficiency of a system by up to 15%. Additionally, the electric motor that drives the pump is typically coupled directly or through a gearbox, providing the necessary rotational energy. The seals and bearings play crucial roles in ensuring the pump's longevity; seals prevent fluid leakage while bearings support the impeller and maintain alignment, significantly affecting the pump's operational reliability and maintenance needs.
Understanding these components is vital as they directly influence the pump's performance parameters, such as flow rate, head pressure, and energy consumption. Data from industry studies suggest that regular maintenance and monitoring of these components can lead to improved efficiency and a reduction in energy costs by as much as 20% in centrifugal pump operations.
Applications and Uses of Centrifugal Pumps

Centrifugal pumps are widely used in various industries due to their efficiency and effectiveness in transferring fluids. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global centrifugal pumps market is expected to reach USD 37.78 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 4.3% from 2019 to 2026. This growth is driven by the increasing demand in sectors such as water and wastewater management, agriculture, and oil and gas.
In the water treatment sector, centrifugal pumps play a crucial role in the distribution and circulation of water, ensuring efficient processing for both municipal and industrial applications. These pumps are essential for transporting wastewater to treatment facilities, as well as for water supply systems that require consistent pressure. Moreover, in the agriculture field, they are employed in irrigation systems to efficiently move water from reservoirs to fields, maximizing crop yield and resource management.
Centrifugal pumps are also extensively utilized in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, where they handle various fluids ranging from corrosive chemicals to high-viscosity substances. Their design allows for continuous operation and easy maintenance, making them an ideal choice for processes that require reliability and precision. As industries increasingly focus on sustainability and efficiency, there is a growing trend toward the use of advanced centrifugal pump designs that enhance performance while reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are popular in various industries for their efficiency and effectiveness in fluid transportation. One of the primary advantages of centrifugal pumps is their ability to handle a wide range of flow rates. They are relatively easy to maintain and operate, making them suitable for continuous and automated processes. Additionally, these pumps can be designed to work with different fluids, including water, chemicals, and slurries, which enhances their versatility in numerous applications.
However, centrifugal pumps are not without their drawbacks. They are generally less effective at pumping very viscous fluids compared to positive displacement pumps. Moreover, they can experience issues with cavitation, which occurs when the pressure of the liquid falls below its vapor pressure, leading to pump damage. Maintenance costs can also increase if the pump is not properly selected for the application, as running an improperly sized centrifugal pump can lead to decreased efficiency and equipment failure.
Tips: When selecting a centrifugal pump, always consider the fluid characteristics and the specific operational demands of your application. Regular maintenance checks can prevent cavitation and improve the longevity of the pump, ensuring it operates at optimal efficiency.
Centrifugal Pump Efficiency and Flow Rate
This chart illustrates the performance metrics of a centrifugal pump, showcasing the flow rate, efficiency, and power consumption. The flow rate is at 100 m³/h with an efficiency of 85% and a power consumption of 20 kW, highlighting the pump's operational characteristics.
Related Posts
-

How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump for Your Industrial Applications
-
How to Choose the Right Centrifugal Pump for Your Industrial Needs
-

How to Choose the Right Air Operated Diaphragm Pump for Your Applications
-

How to Choose the Right Double Diaphragm Pump for Your Application
-

How to Choose the Best Diesel Tank with Pump for Your Needs
-

Maximizing Efficiency and Safety with Diesel Transfer Tanks Featuring Pumps in the Fuel Industry