Essential Tips for Choosing a Gasoline Transfer Pump?
Choosing the right gasoline transfer pump can be challenging. This equipment is vital for transferring fuel safely and efficiently. With various models available, selecting one that suits your needs requires careful consideration.
Different applications demand different features. Some pumps are designed for high flow rates, while others focus on portability. Understanding your requirements is key. Think about where you will use the pump. Will it be at home or on a job site? Take note of the power source as well. Electric and manual options have distinct benefits.
Not all pumps are created equal. Users must evaluate quality and reviews. Read customer feedback to find common issues. A pump that looks great may have hidden flaws. Ensure it meets safety regulations to avoid hazards. Your choice reflects both your needs and values in fueling efficiency.

Understanding the Different Types of Gasoline Transfer Pumps
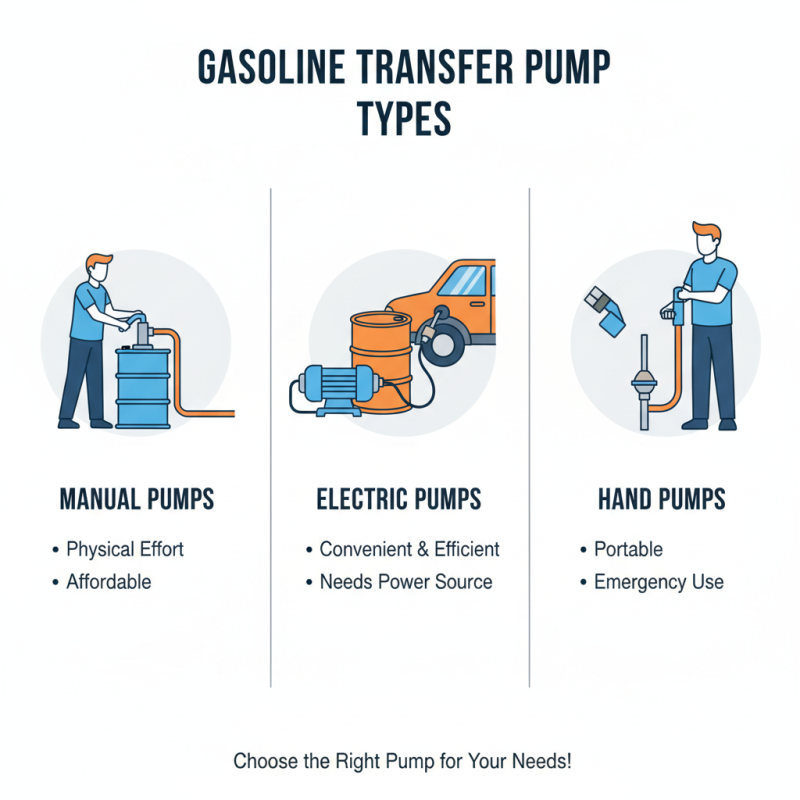
When choosing a gasoline transfer pump, understanding the types can significantly affect your decision. There are several options available. Manual pumps require physical effort but are often affordable. Electric pumps are convenient and efficient but may need a power source. Hand pumps are portable, making them great for emergencies.
Consider the pump's flow rate. A higher flow rate means faster transfer. But this often requires more power. Think about your storage needs too. Some pumps are designed for smaller containers, while others can handle larger tanks. Make sure you pick one that suits your situation.
Tips: Assess the material of the pump. Durable materials ensure longevity. Don't overlook safety features either. Check for automatic shut-off systems. These features can prevent spills. Think about your budget. A cheaper pump may not last long; this can lead to higher costs later.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Gasoline Transfer Pump
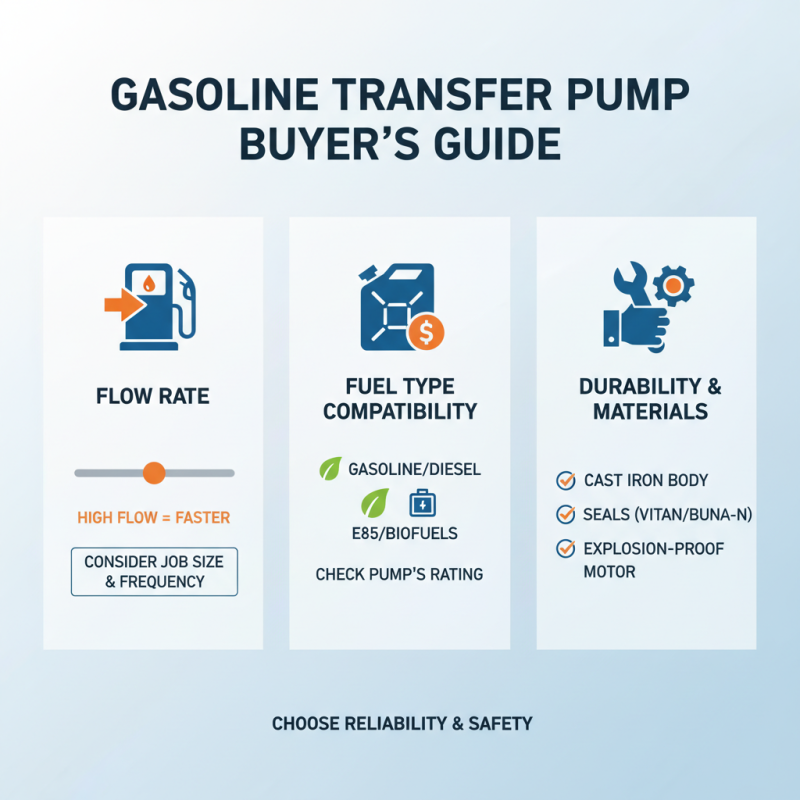
Choosing a gasoline transfer pump requires attention to several key factors. First, consider the pump's flow rate. This determines how quickly you can transfer fuel. A pump with a higher flow rate can save time, especially for large jobs. However, your specific needs will dictate the right flow rate. Think about how often you'll use the pump.
Another important factor is the pump’s construction material. Many pumps are made from aluminum or thermoplastic. Each material has its pros and cons. Aluminum is durable and resistant to corrosion, but it may be heavier. In contrast, thermoplastic can be lighter but might not withstand harsh conditions as well. Consider your environment and the frequency of your pump's use.
Don't forget the pump's safety features. Look for built-in shut-off valves and automatic shut-off controls. These can prevent spills and leaks, protecting you and your surroundings. Ensure that you are comfortable with the installation and operation requirements. Complicated setups can lead to frustration. Check if the pump is easy to maintain and clean, too.
Evaluating Flow Rate and Capacity for Your Needs
When selecting a gasoline transfer pump, flow rate and capacity are key factors. Flow rate determines how quickly fuel moves from one place to another. A higher flow rate means faster transfer, but it may not always be necessary for your requirements. For smaller tasks, a pump with a lower flow rate may suffice. Keep in mind that higher speeds can lead to spills or accidents if not monitored closely.
Capacity is equally crucial. You need a pump that can handle the volume of fuel you typically transfer. A pump with too small a capacity can be frustrating, as it may require frequent refills. Conversely, an overly large pump might be unnecessary for occasional use, making it less economical. It’s essential to consider how often you will use the pump and for what purposes. Assess your specific needs carefully to avoid potential disappointments.
Think about the environment where you’ll use the pump. Will you be transferring fuel indoors or outdoors? Understanding your working conditions can impact your choice. Take time to reflect on these aspects. A thoughtful selection process today can lead to better efficiency tomorrow.
Flow Rate and Capacity of Gasoline Transfer Pumps
Safety Features to Look for in a Gasoline Transfer Pump
When choosing a gasoline transfer pump, safety features are crucial. Look for an automatic shut-off feature. This can prevent overflow and spills. An emergency stop button is also essential. It allows for quick action during unexpected situations. Consider pumps with anti-static features as well. They help minimize fire risks during operation.
Check for certifications. Pumps that meet safety standards provide reassurance. Hoses should be durable and resistant to chemicals. Look for pumps with built-in filters to avoid contamination. A clear display for fuel levels is helpful as well. Evaluate the pressure settings, ensuring they are adjustable.
Some pumps may lack sufficient grounding methods. This can lead to dangerous scenarios. Pay attention to design flaws that might cause leaks. Common mistakes are selecting a pump based solely on price. Always prioritize safety alongside cost. This is vital for securing a safe working environment.
Essential Tips for Choosing a Gasoline Transfer Pump - Safety Features to Look for in a Gasoline Transfer Pump
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Automatic Shut-off | Automatically stops the pump when the tank is full. | Prevents spillage and overfilling. |
| Leak-proof Design | Includes seals and fittings to avoid leaks. | Reduces environmental hazards and fire risks. |
| Grounding Wire | Prevents static electricity build-up. | Minimizes the risk of ignition. |
| Overload Protection | Automatically shuts down if the pump is overloaded. | Protects the pump from damage and ensures safe operation. |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Releases excess pressure in the system. | Prevents pump and line damage, enhancing safety. |
Maintenance Tips for Maximizing Pump Efficiency and Longevity
Maintaining a gasoline transfer pump is crucial for its efficiency and lifespan. Regular inspections can reveal early signs of wear. Check hoses and fittings for leaks. A small drip can lead to bigger issues. Replace worn parts promptly. It’s better to fix minor problems than to wait until they worsen.
Filtration is another key aspect of maintenance. A clean filter keeps contaminants from damaging the pump. Change it frequently, especially if you're transferring fuels that may have impurities. Remember, a clogged filter can reduce performance significantly.
Storage is often overlooked. If you’re not using the pump regularly, ensure it's kept in a cool, dry place. Exposure to extreme temperatures can shorten its life. Some users forget to drain any residual fuel, which can lead to corrosion. Reflect on your current practices and make adjustments as needed. Regular maintenance ensures the pump operates at peak performance when you need it the most.
Related Posts
-

Top 5 Gas Transfer Pumps for Efficient Fuel Transfer and Handling
-

How to Choose the Right Transfer Tank Pump for Your Needs in 2025
-

7 Reasons to Choose a Diesel Transfer Tank with Pump for Your Business
-

How to Choose the Right Fuel Transfer Tank with Pump for Your Needs
-

Everything You Need to Know About Transfer Tank Pumps: Your Ultimate Guide to Safe Fuel Handling
-

How to Choose the Best Fuel Transfer Tank with Pump for Your Needs