How to Choose the Right Gas Transfer Pump for Your Industrial Needs
Selecting the appropriate gas transfer pump for industrial applications is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and safety. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global gas transfer pump market is projected to reach $7.96 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including oil and gas, chemicals, and environmental applications. As industries seek to optimize their processes and reduce downtime, understanding the specific requirements for gas transfer pumps, such as flow rate, pressure, and compatibility with different gases, becomes essential. With a multitude of options available in the market, including diaphragm pumps, rotary vane pumps, and positive displacement pumps, choosing the right gas transfer pump can significantly impact productivity and cost-efficiency. This guide aims to equip you with the necessary insights to make an informed decision tailored to your industrial needs.
Identifying Your Specific Industrial Requirements for Gas Transfer Pumps
When selecting the right gas transfer pump for industrial applications, it is crucial to first identify specific operational requirements. Consider the types of gases to be transferred, their characteristics, and the environmental conditions in which the pump will operate. Factors such as flow rate, pressure capabilities, and the required durability should be assessed to ensure the pump can meet the demands of the job. Additionally, understanding compliance with industry regulations and safety standards is essential.

Recent advancements in pump technology highlight the importance of choosing a solution that not only meets existing needs but also incorporates innovative features. For instance, smart technology can optimize fuel transfer processes, enhancing efficiency and productivity. This trend underscores the necessity of evaluating modern solutions that provide continuous-duty capabilities and intelligent monitoring systems, allowing for better management of fueling operations and ultimately supporting a more streamlined industrial workflow.
Understanding the Different Types of Gas Transfer Pumps Available
When it comes to selecting a gas transfer pump for industrial applications, understanding the different types available is crucial. Generally, gas transfer pumps can be categorized into positive displacement pumps and centrifugal pumps. Positive displacement pumps are ideal for high-viscosity fluids and provide a consistent flow, making them suitable for tasks that require precise fluid handling. They work by trapping a fixed amount of gas and forcing it into the discharge pipe, creating a steady flow regardless of variations in pressure.
On the other hand, centrifugal pumps are more common for transferring gases at lower pressures. They utilize a rotating impeller to impart velocity to the gas, which is then converted to pressure in the pump casing. These pumps excel in applications requiring large volumes of gas transfer and are often favored for their efficiency in moving gases across considerable distances. Additionally, it's essential to consider the material construction of the pump, as it will greatly affect compatibility with the specific gases being transferred. Selecting the right type involves analyzing the operational pressure, flow rate, and the physical properties of the gas to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the pump.
Evaluating Key Performance Metrics for Optimal Pump Selection
When selecting a gas transfer pump for industrial applications, evaluating key performance metrics is crucial to ensure optimal functionality and efficiency. First and foremost, flow rate is a critical metric that determines the volume of gas the pump can handle over a specific time. Depending on your operational needs, you may require a pump with a high flow rate for rapid transfer or a more controlled flow for precision applications. Understanding the gas characteristics—such as viscosity, density, and chemical composition—also plays a vital role in selecting a pump that can accommodate these factors without compromising performance.
Another essential aspect to consider is the pump's pressure rating, which should align with the system requirements to prevent operational failures. Pressure fluctuations can affect the transfer process, so a pump with a robust pressure tolerance is necessary for consistent performance. Additionally, compatibility with various gas types will ensure that the pump materials are resistant to corrosion or degradation, particularly when dealing with aggressive chemicals. By carefully analyzing these performance metrics, you can select a gas transfer pump that not only meets your industrial needs but also enhances operational reliability and efficiency.
Assessing Compatibility with Existing Industrial Systems and Infrastructure
When selecting the right gas transfer pump for industrial applications, it's essential to assess its compatibility with existing industrial systems and infrastructure. As industries transition towards advanced automation technologies, such as those driven by Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), seamless integration becomes critical. Reports indicate that with the emergence of IoT, the market for communication protocols is projected to grow significantly, highlighting the need for devices that can operate within these frameworks.
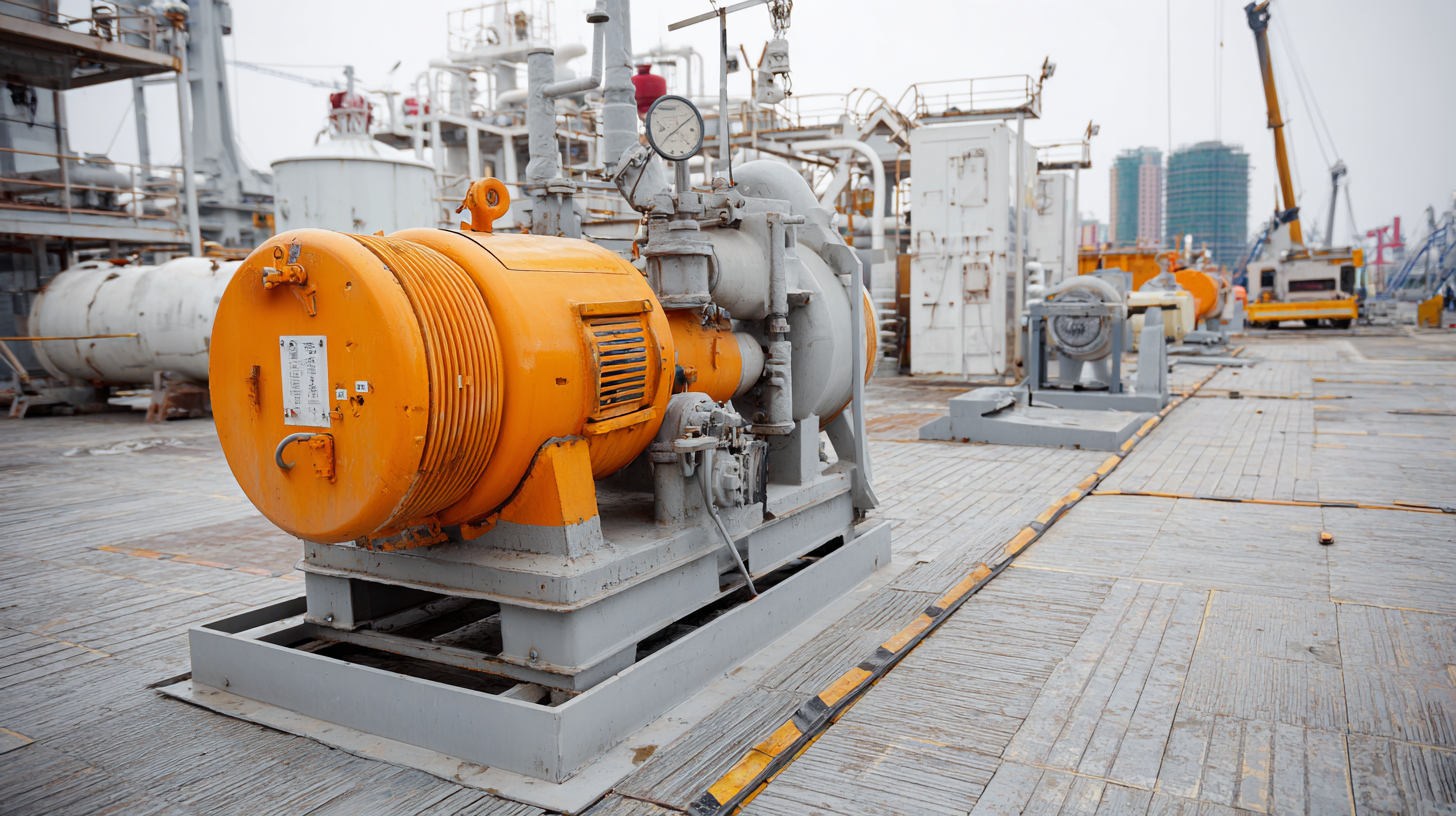

According to industry research, the EMEA compressed oil market for refrigeration is expected to grow at a CAGR of 2.9% from 2024 to 2032, emphasizing the rising demand for efficient and compatible pumping solutions. Furthermore, with over 65% of enterprises in China adopting cloud technologies, the interoperability of gas transfer pumps with cloud-based monitoring and control systems is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency. Ensuring that the selected pump conforms to the specifications of existing infrastructure will facilitate a smoother transition and optimize performance in an increasingly connected industrial landscape.
Reviewing Maintenance and Support Considerations for Long-Term Use
When choosing the right gas transfer pump for industrial use, maintenance and support considerations are of paramount importance for ensuring long-term functionality and reliability. Regular maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of gas transfer pumps, which are critical in various applications such as chemical processing and fuel transfer. According to industry reports, a proactive maintenance approach can reduce operational downtime by as much as 30%, thereby enhancing overall efficiency. Moreover, recognizing the specific needs of your operation can influence your choice of pump; factors such as fluid type, pressure requirements, and environmental conditions should all be taken into account.
Support services are equally crucial in this context. Many professionals advocate for selecting pumps from manufacturers who provide comprehensive support packages, including technical assistance and access to spare parts. A study indicated that companies with robust maintenance and support structures reported a 50% lower total cost of ownership for their equipment. Therefore, when evaluating potential gas transfer pumps, it is essential to consider not only the initial investment but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance and support to ensure a sustainable operation.
How to Choose the Right Gas Transfer Pump for Your Industrial Needs
| Pump Type | Flow Rate (GPM) | Pressure Rating (PSI) | Power Source | Maintenance Frequency (Months) | Support Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diaphragm Pump | 20 | 100 | Electric | 6 | 24/7 |
| Centrifugal Pump | 50 | 150 | Gasoline | 12 | Weekdays 9-5 |
| Positive Displacement Pump | 30 | 200 | Hydraulic | 9 | 24/7 |
| Gear Pump | 25 | 120 | Electric | 12 | Weekdays 8-6 |
Related Posts
-

Unlocking Efficiency and Cost Savings with Advanced Fuel Transfer Pump Solutions
-

How to Select the Right Chemical Pump for Your Industrial Needs
-

How to Choose the Right Chemical Pump for Your Industry Needs
-

7 Reasons to Choose a Diesel Transfer Tank with Pump for Your Business
-

How to Choose the Right Fuel Transfer Tank with Pump for Your Needs
-

Understanding the Benefits of Using Above Ground Diesel Storage Tanks in Various Industries